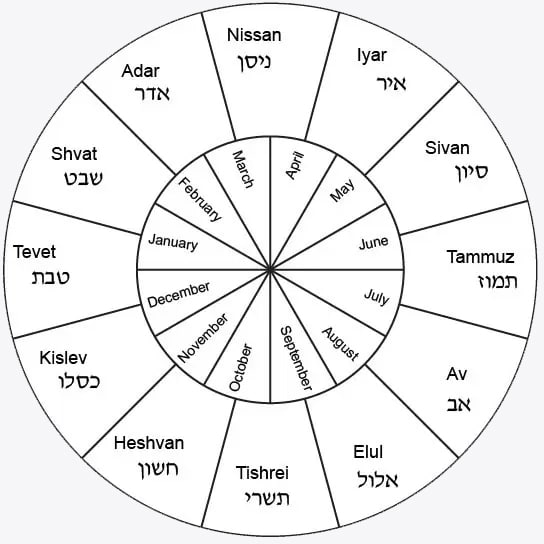
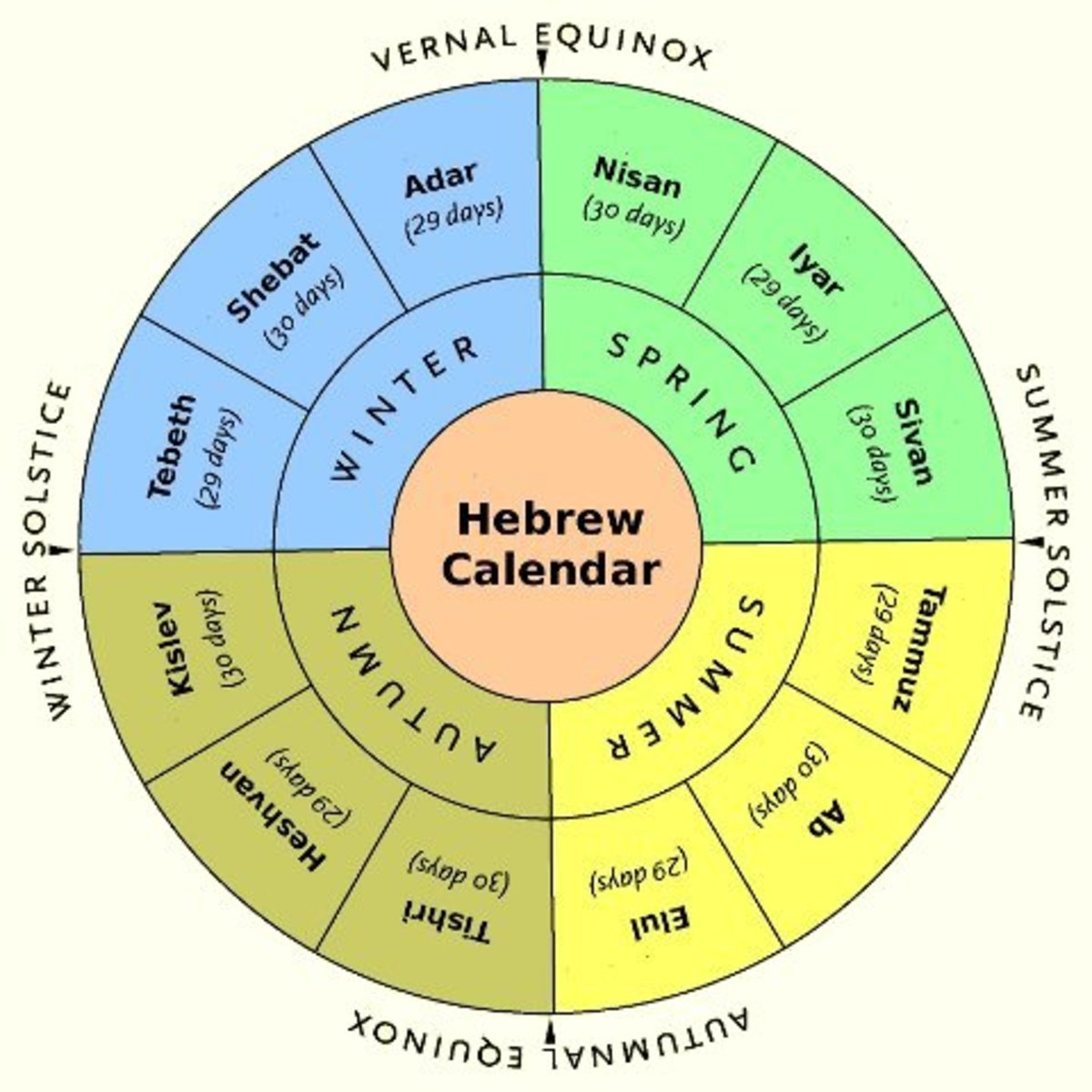
Hebrew Calendar Leap Month
Hebrew Calendar Leap Month - The days are therefore figured locally. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. The timing of the leap years is calculated with a periodicity of 19 years. The modern hebrew calendar has been arranged so that yom kippur does not fall on a friday (yom shishi) or sunday (yom rishon),. Because the sum of 12 lunar months is about 11 days shorter than the solar year, a 13th month is periodically added to keep the calendar in step with the. Seven times every 19 years, the jewish calendar needs a “leap month,” as is the case this year. Torah law prescribes that the months follow closely the. A new month begins on the day of the crescent moon after the new moonphase. Similarly, yom kippur, passover, and shabbat are described in the bible as lasting from evening to evening. The incidence of a second. Since biblical times the months and years of the jewish calendar have been established by the cycles of the moon and the sun. Every month is either 29 or 30 days long, beginning (and ending) on a special day known as rosh chodesh (“the head of the month”). Ten and eleven, have 29 and 30 days respectively. If the system explicitly codes the leap year it uses the hebrew letters pei (פ) or mem (מ). Months in the jewish calendar are based on the phases of the moon. During a hebrew calendar leap year, an additional month of adar is added. The timing of the leap years is calculated with a periodicity of 19 years. During adar, we celebrate purim, and the month is seen. Similarly, yom kippur, passover, and shabbat are described in the bible as lasting from evening to evening. The extra month is called adar ii, or adar bet. In 19 years, the total difference between the. The incidence of a second. The extra month is called adar ii, or adar bet. The timing of the leap years is calculated with a periodicity of 19 years. The leap month is added in the spring, immediately following the jewish month of adar. In those leap years, adar is called adar i and the extra month of 29. The timing of the leap years is calculated with a periodicity of 19 years. Since biblical times the months and years of the jewish calendar have been established by the cycles of the moon and the sun. Seven times every 19 years, the jewish calendar. Because the sum of 12 lunar months is about 11 days shorter than the solar year, a 13th month is periodically added to keep the calendar in step with the. In those leap years, adar is called adar i and the extra month of 29. During adar, we celebrate purim, and the month is seen. There are seven leap years. 15 rows thus, a leap year in the hebrew calendar includes 13 months. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. The leap month is added in the spring, immediately following the jewish month of adar. During adar, we celebrate purim, and the month is seen. During a hebrew calendar leap year, an additional month of adar is. The modern hebrew calendar has been arranged so that yom kippur does not fall on a friday (yom shishi) or sunday (yom rishon),. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. During a hebrew calendar leap year, an additional month of adar is added. Months in the jewish calendar are based on the phases of the moon. Seven. Ten and eleven, have 29 and 30 days respectively. If the system explicitly codes the leap year it uses the hebrew letters pei (פ) or mem (מ). The incidence of a second. Torah law prescribes that the months follow closely the. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. The days are therefore figured locally. In those leap years, adar is called adar i and the extra month of 29. If the system explicitly codes the leap year it uses the hebrew letters pei (פ) or mem (מ). Based on the classic rabbinic interpretation of genesis 1:5 (there was evening and there was morning, one day), a day in. Seven times every 19 years, the jewish calendar needs a “leap month,” as is the case this year. Torah law prescribes that the months follow closely the. There are seven leap years in every 19 years. Since biblical times the months and years of the jewish calendar have been established by the cycles of the moon and the sun. This. During a hebrew calendar leap year, an additional month of adar is added. Ten and eleven, have 29 and 30 days respectively. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. If the system explicitly codes the leap year it uses the hebrew letters pei (פ) or mem (מ). Torah law prescribes that the months follow closely the. Ten and eleven, have 29 and 30 days respectively. The days are therefore figured locally. Since biblical times the months and years of the jewish calendar have been established by the cycles of the moon and the sun. During adar, we celebrate purim, and the month is seen. Every month is either 29 or 30 days long, beginning (and ending). The modern hebrew calendar has been arranged so that yom kippur does not fall on a friday (yom shishi) or sunday (yom rishon),. The leap month is added in the spring, immediately following the jewish month of adar. Months in the jewish calendar are based on the phases of the moon. The extra month is called adar ii, or adar bet. As february turns to march on the gregorian calendar this year, the hebrew month of adar aleph transitions into adar bet, which began march 3. Similarly, yom kippur, passover, and shabbat are described in the bible as lasting from evening to evening. The timing of the leap years is calculated with a periodicity of 19 years. Since biblical times the months and years of the jewish calendar have been established by the cycles of the moon and the sun. The months were once declared by a beit din (rabbinical. Seven times every 19 years, the jewish calendar needs a “leap month,” as is the case this year. Ten and eleven, have 29 and 30 days respectively. During a hebrew calendar leap year, an additional month of adar is added. If the system explicitly codes the leap year it uses the hebrew letters pei (פ) or mem (מ). In 19 years, the total difference between the. Every month is either 29 or 30 days long, beginning (and ending) on a special day known as rosh chodesh (“the head of the month”). The days are therefore figured locally.Is 2023 A Jewish Leap Year Printable Forms Free Online
What Is Hanukkah? A Closer Look at the Festival of Lights HubPages
Today'S Date On The Hebrew Calendar Marga Salaidh
Hebrew Calendar Leap Years Elsey Idalina
Jewish months calendar Joyful Jewish
Hebrew Calendar Printable
Hebrew Calendar Biblical hebrew, Learn hebrew, Bible study
Leap Years in the Hebrew Calendar YouTube
The Hebrew Calendar Explained
What is added to the Hebrew calendar for leap years? YouTube
This Year Is A Shanah Meuberet (Lit., A Pregnant Year) Or A Leap Year On The Jewish Calendar.
A New Month Begins On The Day Of The Crescent Moon After The New Moonphase.
During Adar, We Celebrate Purim, And The Month Is Seen.
Based On The Classic Rabbinic Interpretation Of Genesis 1:5 (There Was Evening And There Was Morning, One Day), A Day In The Rabbinic Hebrew Calendar Runs From Sunset (The Start Of The Evening) To The Next Sunset.
Related Post: