Why Is The Jewish Calendar Different
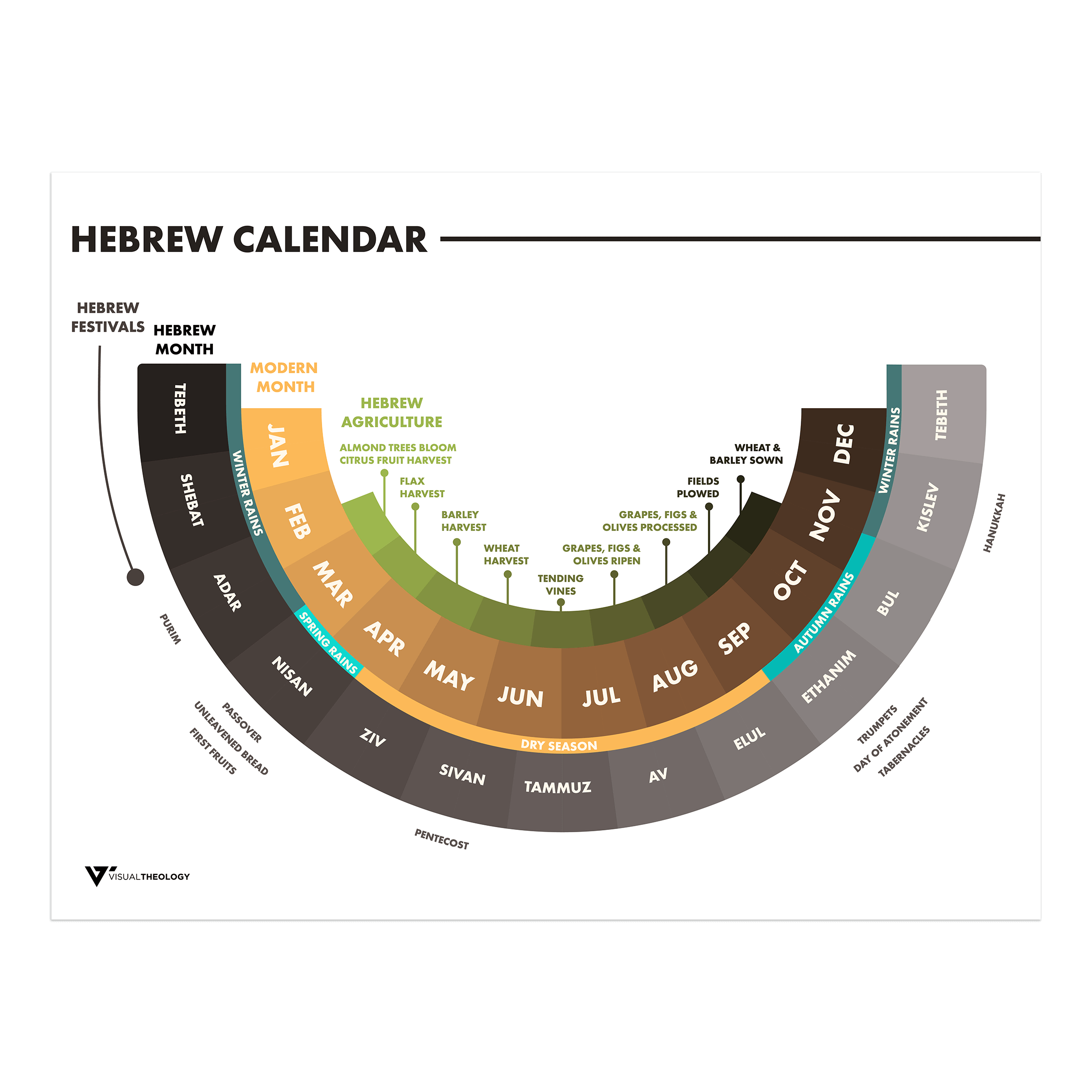
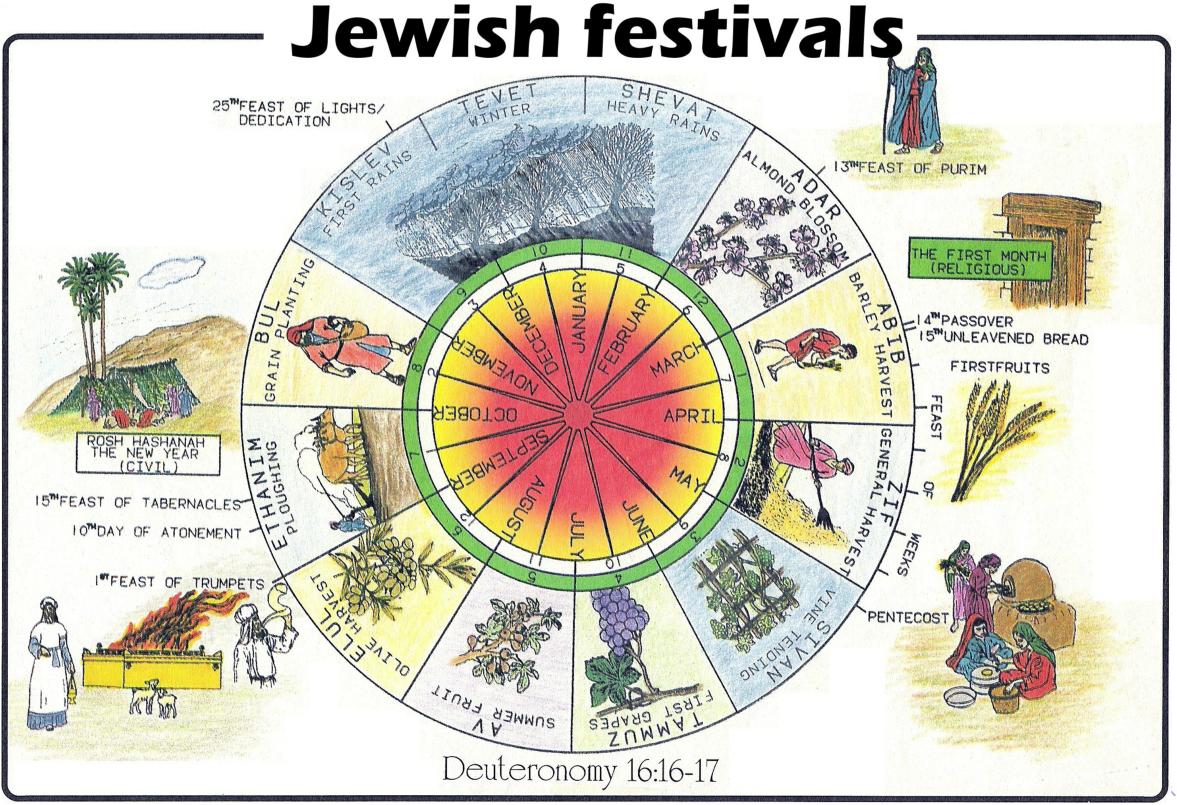
Why Is The Jewish Calendar Different - Corresponding with all of the lunisolar calendars means that the jewish calendar is in sync with the natural cycles of the moon and the sun. In israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official. The jewish year begins in the fall with. The exact origins of the jewish calendar are. The months of the jewish calendar are tishrei, marheshvan, kislev, tevet, shevat, adar, nissan, iyar, sivan, tammuz, av, and elul. The jewish calendar counts the time from the year 3761 b.c., the date for the creation of the world and the universe, according to the bible. This unique calendar has been in use for. Similarly, the jewish calendar has different starting points for different purposes. Jews started using ve in the 1800s to designate the western calendar since the jewish one was by then quite different. The holidays are late this year or the holidays are early this year. in fact, the holidays never are early or late; The basic factor upon which the lunisolar calendar is based, the average length of the lunar month, would have taken more than two centuries of measurement and observation to. The jewish or hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar created and used by the hebrew people—it’s “lunar” in that every month follows the phases of the moon, and “solar”. Why do christians in the east usually celebrate easter on a different day than those in the west? The jewish calendar has the following months: The jewish calendar counts the time from the year 3761 b.c., the date for the creation of the world and the universe, according to the bible. The holidays are late this year or the holidays are early this year. in fact, the holidays never are early or late; The months of the jewish calendar are tishrei, marheshvan, kislev, tevet, shevat, adar, nissan, iyar, sivan, tammuz, av, and elul. At the time, some areas followed the jewish calendar more closely, and the. They just follow a different calendar. The jewish calendar, also known as the hebrew calendar, is a unique and significant part of jewish culture and tradition. Simply put, the jewish calendar is where the. The months of the jewish calendar are tishrei, marheshvan, kislev, tevet, shevat, adar, nissan, iyar, sivan, tammuz, av, and elul. The jewish or hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar created and used by the hebrew people—it’s “lunar” in that every month follows the phases of the moon, and “solar”. The jewish calendar. Similarly, the jewish calendar has different starting points for different purposes. These astronomical phenomena helped determine the length. Different from other biblical holidays, the date for shavuot is not explicitly fixed in the torah. In israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official. The exact origins of the jewish calendar are. The jewish calendar is lunisolar, just like the ancient macedonian, babylonian, egyptian, and chinese calendars. The jewish calendar has the following months: In israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official. The months of the jewish calendar are tishrei, marheshvan, kislev, tevet, shevat, adar, nissan, iyar, sivan, tammuz, av, and elul.. The jewish calendar is lunisolar, just like the ancient macedonian, babylonian, egyptian, and chinese calendars. The hebrew, or jewish, calendar is both a solar and lunar calendar, as opposed to the gregorian, or civil, calendar which is based on a solar year that is divided into 12 months. Most of the world uses the gregorian calendar, which is based on.. The jewish calendar counts the time from the year 3761 b.c., the date for the creation of the world and the universe, according to the bible. Jews started using ve in the 1800s to designate the western calendar since the jewish one was by then quite different. Similarly, the jewish calendar has different starting points for different purposes. The exact. Most of the world uses the gregorian calendar, which is based on. They just follow a different calendar. The basic factor upon which the lunisolar calendar is based, the average length of the lunar month, would have taken more than two centuries of measurement and observation to. Jews started using ve in the 1800s to designate the western calendar since. Most of the world uses the gregorian calendar, which is based on. Why does the jewish calendar change every year? The jewish calendar counts the time from the year 3761 b.c., the date for the creation of the world and the universe, according to the bible. The basic factor upon which the lunisolar calendar is based, the average length of. The jewish calendar counts the time from the year 3761 b.c., the date for the creation of the world and the universe, according to the bible. The jewish or hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar created and used by the hebrew people—it’s “lunar” in that every month follows the phases of the moon, and “solar”. In leap years, adar has. Different from other biblical holidays, the date for shavuot is not explicitly fixed in the torah. Similarly, the jewish calendar has different starting points for different purposes. In leap years, adar has 30 days. While rosh hashanah marks the creation of the world, the month of nisan in spring is considered the first. These astronomical phenomena helped determine the length. This unique calendar has been in use for. Jews started using ve in the 1800s to designate the western calendar since the jewish one was by then quite different. Why does the jewish calendar change every year? It determines the dates of jewish holidays and other rituals, such as yahrzeits and the schedule of public torah readings. Different from other. Instead, it is observed on the day following the 49th and final day in the counting of the omer. Why does the jewish calendar change every year? Why do jewish holidays change dates every year? This makes it different from other calendars, such as the gregorian. The jewish or hebrew calendar is a lunisolar calendar created and used by the hebrew people—it’s “lunar” in that every month follows the phases of the moon, and “solar”. The hebrew, or jewish, calendar is both a solar and lunar calendar, as opposed to the gregorian, or civil, calendar which is based on a solar year that is divided into 12 months. The jewish calendar, also known as the hebrew calendar, is a unique and significant part of jewish culture and tradition. In israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official. The jewish calendar isn't just a tool for observing the passage of time. The holidays are late this year or the holidays are early this year. in fact, the holidays never are early or late; The jewish calendar has the following months: The basic factor upon which the lunisolar calendar is based, the average length of the lunar month, would have taken more than two centuries of measurement and observation to. In leap years, adar has 30 days. The jewish year begins in the fall with. Jews started using ve in the 1800s to designate the western calendar since the jewish one was by then quite different. Similarly, the jewish calendar has different starting points for different purposes.Rosh Hashanah And The Hebrew Lunar Calendar The Mathematics Behind
Hebrew Calendar Visual Theology
The Jewish Calendar Exclusive Israel Tours
What Is The Seventh Month In Jewish Calendar Calendar Productivity Hacks
Why is the Jewish Calendar Different
Jewish Holiday Calendar 20222023
Understanding The Jewish Calendar Jania Lisetta
What is the difference between the Hebrew and Gregorian calendars
The Jewish Year in a Nutshell Letters to Josep
Why Is The Jewish Calendar Different
They Just Follow A Different Calendar.
The Months Of The Jewish Calendar Are Tishrei, Marheshvan, Kislev, Tevet, Shevat, Adar, Nissan, Iyar, Sivan, Tammuz, Av, And Elul.
Why Do Christians In The East Usually Celebrate Easter On A Different Day Than Those In The West?
Different From Other Biblical Holidays, The Date For Shavuot Is Not Explicitly Fixed In The Torah.
Related Post: